Ever felt nervous before a date? Worried about an interview? Panicky before giving a speech? Sweaty palms, heart pounding, thoughts racing? We all feel anxiety from time to time, sometimes even with physical symptoms, but some people have anxiety so bad that it takes over their lives. Imagine feeling nervous and worried all the time? Anxiety can be debilitating, affecting a person’s ability to function at work, school and home. Symptoms can be specific to a situation, a fear or it can be more pervasive and ever present; symptoms can be mild to intense, sometimes requiring immediate medical attention.
Anxiety can manifest in a multitude of ways, including: worry, tension, rumination, obsessive thoughts, intrusive thoughts, tics, odd behaviors, avoidance, panic, absenteeism, to begin. Symptoms can present physically, such as stomachaches, headaches, racing heart, pressured speech, difficulty sleeping, restlessness, agitation, sweating, heart pounding, vomiting, shortness of breath and nausea. Or it can present in behaviors like nail biting, hand washing, pulling hair out, refusing to do certain activities, work or school refusal, isolation, withdrawal, tics and repetitive behaviors.
Anxiety can be acute, pervasive and chronic. It can be tied to specific situations or generalized to all areas of life. The list is overwhelming, much like anxiety feels overwhelming. Although broad and varied, anxiety tends to manifest in predictable ways and are categorized into the following types of panic and anxiety disorders.
Types of Panic & Anxiety Disorders
Panic Disorder
Panic Disorder is described as recurrent unexpected anxiety attacks that result in a persistent fear or worry about having another attack, worry about losing control, having a heart attack or going crazy, or change in behavior related to the panic attacks.
A panic attack can be defined as a period of intense fear or discomfort characterized by physical complaints (racing heart, sweating, shaking, difficulty breathing, nausea, stomach ache, dizzy, chills, hot flush), numbness, derealization (feel “unreal”), depersonalization (feel detached), fear of losing control or dying.
Panic disorder is further differentiated between panic attacks with or without agoraphobia. Agoraphobia consists of anxiety about certain situations or places where escape is difficult or embarrassing, such as outside the home alone, being in a crowd, standing in line, being on a bridge or traveling in a bus, train, or car.

Specific Phobias
Specific phobias are a type of anxiety disorder that is characterized by a specific fear of an object or situation, such as flying, heights, animals, getting a shot, seeing blood, etc that is avoided at great lengths. The fear is often unreasonable to the situation or object as the person who is afraid is not in any actual danger, but the persistent fear is excessive and can even involve extreme reactions at the thought of the feared object or situation.
Social Phobia
Social phobia is a marked and persistent fear of social situations in which people fear being criticized, embarrassed or humiliated in some way. Fearing scrutiny by others, settings that involve other people or their own performance can evoke fear and avoidance reactions that can lead to panic attacks when anticipating or experiencing social situations. Some people are able to attend social functions, although they do so with considerable anxiety and discomfort. Reactions in children can be slightly different and include crying, freezing, temper tantrums and refusal to attend social functions.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Anxiety can also manifest in a more generalized manner, such as seen with Generalized Anxiety Disorder. The anxiety and worry are excessive and difficult to control and can include feelings of apprehensive expectation, or an inability to relax at all. Common symptoms include feeling on edge, restlessness, easily tired, mind going blank, difficulty concentrating, irritability, muscle tension and trouble falling or staying asleep.
With generalized anxiety, the feelings of worry and tension are not tied to any specific situation, object or problem. Instead, people feel as if they cannot relax or control worrying, often overthinking many if not most things. And while people can have characteristics of other anxiety disorders, their symptoms are pervasive in all areas. For example, someone worried about an upcoming presentation may worry about their performance, they do not have symptoms in most social settings. Rather, they worry about every task they have to complete in many different settings.
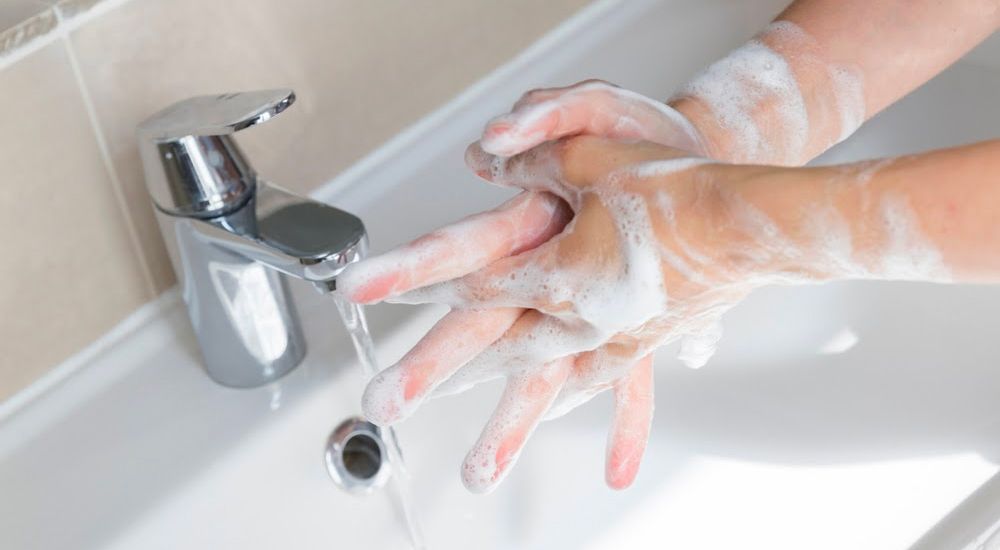

Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
Although no longer part of the anxiety disorders in the DSM-5, OCD has a significant anxiety component that warrants an inclusion in this article. OCD is characterized by persistent intrusive thoughts that cause extreme feelings of anxiety that are relieved through the adoption of compulsions as a means of coping with the anxiety. Compulsions are behaviors, often repetitive, and can include hand washing, counting, praying repeating words to themselves, checking, and ordering. These behaviors and mental tasks, when completed, allow the person some relief from their anxiety. If not completed, cause significantly increased anxiety.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Another disorder that has a significant anxiety component is post-traumatic stress disorder or PTSD. Although no longer part of the anxiety disorders in the DSM-5, the severity of the anxiety experienced warrants inclusion in a complete list of anxiety disorders. PTSD is most notable as a disorder that results following a traumatic event in which the person fears for the death of themselves or someone else. The experience of trauma can result from their own experience, witnessing the trauma of someone else or hearing about the trauma of others. This can also include threats of harm to self or others. The experience causes intense fear, helplessness or horror.
The symptoms of PTSD include re-experiencing the trauma through intrusive thoughts, memories or dreams with intense distress where one feels as if they are reliving the event or intense anxiety upon exposure to reminders of the trauma. People often avoid thinking about the event even to the point that they don’t remember details and will go to great lengths to avoid the place or anything that reminds them of the event. They can also feel a sense of detachment from others, have difficulty envisioning their future and feelings of numbness or difficulty feeling the normal range of feelings. Physical symptoms of anxiety can include difficulty sleeping, irritability, trouble concentrating, an exaggerated startle response and hyper-vigilance.
Conclusion
Anxiety causes intense distress and can manifest in a variety of ways as detailed above. However, there is hope and effective treatments for all types of anxiety disorders. Research demonstrates that both psychotherapy and medication together is the most effective method of treatment. If you suspect that you or a loved one may have an anxiety disorder, please reach out to a mental health professional for treatment. Relief is possible, as is complete remittance of symptoms.